
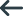

You can compile the preceding program with just the CREATEXFD directive to generate the XFD. The compiled program will run and will build the database table shown at the end of this section.
Here's how the database table is built. First, any fields listed in the KEY IS clause of the SELECT are included ("p-o-number" in this example). Then the Compiler takes the largest record ("p-o-detail-record") and lists the fields that make up that record. The rest of this section shows the specific fields that are placed into the table.
All of the data from the COBOL program is stored in and retrieved from the database, even though not all fields are explicitly named in the database table. For a description of how this works, see the chapter XFDs.
The underlined fields are the only ones that will be entered into the table:
fd p-o-file.
01 p-o-record.
03 p-o-division-number pic 9(3).
03 p-o-record-type pic x.
88 header-record value "h".
88 detail-record value "d".
03 p-o-number pic 9(10).
03 p-o-number-detail redefines p-o-number.
05 picking-ticket-number pic 9(6).
05 shipping-region pic 9(2).
05 p-o-customer-type pic 9(2).
05 p-o-customer-breakdown redefines
p-o-customer-type.
07 customer-category pic x.
88 p-o-customer-retail value "r".
88 p-o-customer-whlsale value "w".
07 customer-pay-format pic x.
88 is-net-30 value "3".
88 is-net-10 value "1".
03 p-o-date.
05 p-o-yy pic 9(2).
05 p-o-mm pic 9(2).
05 p-o-dd pic 9(2).
01 p-o-detail-record.
03 p-o-dept-number pic 9(3).
03 p-o-record-type pic x.
03 detail-p-o-number pic 9(10).
03 p-o-shipping-info.
05 p-o-quantity-to-ship pic s9(4) comp.
05 p-o-total-quantity pic s9(4) comp.
03 p-o-notes.
05 notes-line occurs 3 times pic x(40).
As the table is built:
The following table is built in the database:
* The actual database datatype may vary.
For a list of supported data types and their COBOL equivalents, see the Limits and Ranges section found in the appendix of this manual that is specific to your RDBMS.