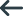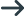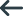
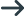

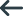
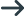

Before a cursor can be used, it must be declared. This is done using the DECLARE CURSOR statement in which you specify a name for the cursor and either a SELECT statement or the name of a prepared SQL statement.
Cursor names must conform to the rules for identifiers on the database that you are connecting to, for example, some databases do not allow hyphens in cursor names.
EXEC SQL
DECLARE Cur1 CURSOR FOR
SELECT first_name FROM employee
WHERE last_name = :last-name
END-EXEC
This example specifies a SELECT statement using an input host variable (:last-name). When the cursor OPEN statement is executed, the values of the input host variable are read and the SELECT statement is executed.
EXEC SQL
DECLARE Cur2 CURSOR FOR stmt1
END-EXEC
. . .
move "SELECT first_name FROM emp " &
"WHERE last_name=?" to prep.
EXEC SQL
PREPARE stmt1 FROM :prep
END-EXEC
. . .
EXEC SQL
OPEN Cur2 USING :last-name
END-EXEC
In this example, the DECLARE CURSOR statement references a prepared statement (stmt1). A prepared SELECT statement can contain question marks (?) which act as parameter markers to indicate that data is to be supplied when the cursor is opened. The cursor must be declared before the statement is prepared.